“Where the engine sits matters!” Understanding Motor Layout in Cars: A Key to Performance and Driving Dynamics
Last Updated At: 2026-02-23 Author: Sarah
[Car Tech Knowledge/ XNmotors]
When purchasing a car, enthusiasts and buyers often encounter terms like “front-engine,” “mid-engine,” or “rear-engine,” referring to the motor layout of a vehicle. But what exactly does “motor layout” mean, and why is it important when choosing your next car? Let’s explore this foundational aspect of automotive design and how it impacts performance, handling, and everyday usability.

Image Source: AI generated
What is Motor Layout?
The motor layout of a car describes the physical position of the engine (or motor in electric vehicles) relative to the vehicle’s chassis and drivetrain. Essentially, it tells you where the engine is placed—whether in the front, middle, or rear of the car—and how power is delivered to the wheels (front-wheel, rear-wheel, or all-wheel drive).
This layout directly affects weight distribution, center of gravity, and how the car handles, accelerates, and brakes. Engineers carefully design the motor layout to balance these factors based on the car’s purpose—whether for performance, efficiency, or practicality.
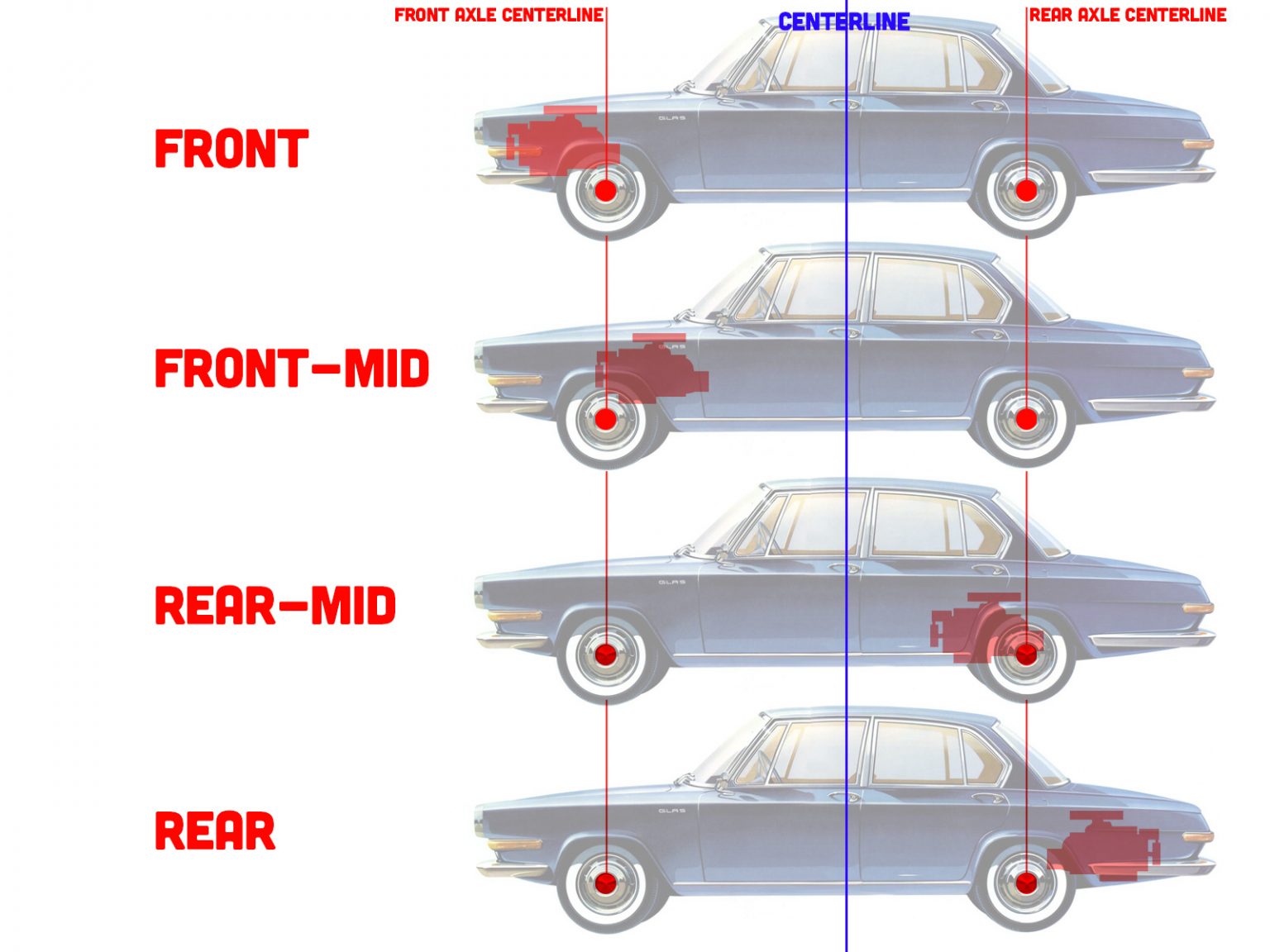
Image Source: World Wide Web
Types of Motor Layouts in Cars
1. Front-Engine Layout
In a front-engine layout, the engine is positioned over or in front of the front axle. This is the most common design in modern cars due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and space efficiency.

Image Source: AI generated
Advantages:
• Allows for more passenger and cargo space.
• Easier to manufacture and maintain.
• Offers better traction in front-wheel-drive systems, especially in slippery conditions.
Common Applications:
• Everyday sedans, hatchbacks, SUVs, and most economy cars.
Example: Toyota Corolla, Honda CR-V
2. Mid-Engine Layout
The mid-engine layout places the engine between the front and rear axles, typically behind the passenger cabin. This design creates a nearly perfect weight balance for exceptional handling and stability.
Image Source: AI generated
Advantages:
• Superior weight distribution, resulting in better cornering and traction.
• Lower center of gravity improves overall performance.
Disadvantages:
• Reduced cabin and cargo space.
• Often more expensive and complex to produce.
Common Applications:
• High-performance sports cars and supercars.
Example: Ferrari 488, Porsche 718 Cayman
3. Rear-Engine Layout
In a rear-engine layout, the engine sits behind the rear axle. This design is less common but is iconic in certain brands and models, especially those focused on unique driving dynamics.

Image Source: AI generated
Advantages:
• Provides strong rear-wheel traction during acceleration.
• Compact drivetrain layout improves interior space.
Disadvantages:
• Weight imbalance can make handling tricky, especially for inexperienced drivers.
• Reduced stability at high speeds without advanced engineering solutions.
Common Applications:
• High-performance sports cars and niche vehicles.
Example: Porsche 911, classic Volkswagen Beetle
Impact on Drive Systems
Motor layouts work in tandem with the car’s drivetrain, which defines how power is distributed to the wheels:
• Front-wheel drive (FWD): Most common with front-engine layouts, offering efficiency and better traction for daily use.
• Rear-wheel drive (RWD): Typically paired with rear- or mid-engine layouts, delivering sporty performance and precise handling.
• All-wheel drive (AWD): Often adaptable to multiple motor layouts, providing balanced power to all four wheels for enhanced grip and off-road capabilities.
Why Does Motor Layout Matter?
The motor layout isn’t just an engineering choice—it significantly impacts how a car feels and performs. For instance:
• Daily Drivers: Front-engine, front-wheel-drive cars excel in fuel efficiency and practicality.
• Sports Cars: Mid-engine or rear-engine layouts deliver dynamic handling and agility for high-speed driving.
• Off-Road Vehicles: Front-engine AWD systems ensure traction on uneven terrain.
When choosing a car, understanding its motor layout helps you align its capabilities with your driving needs and preferences.
Motor Layout in Electric Vehicles
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), the traditional concept of motor layout is evolving. Electric motors are smaller and can be positioned near any axle, allowing manufacturers to design cars with multiple motors (one for each axle) for improved efficiency and power distribution.
Example: Tesla Model S (dual-motor AWD layout), Rivian R1T (quad-motor layout).
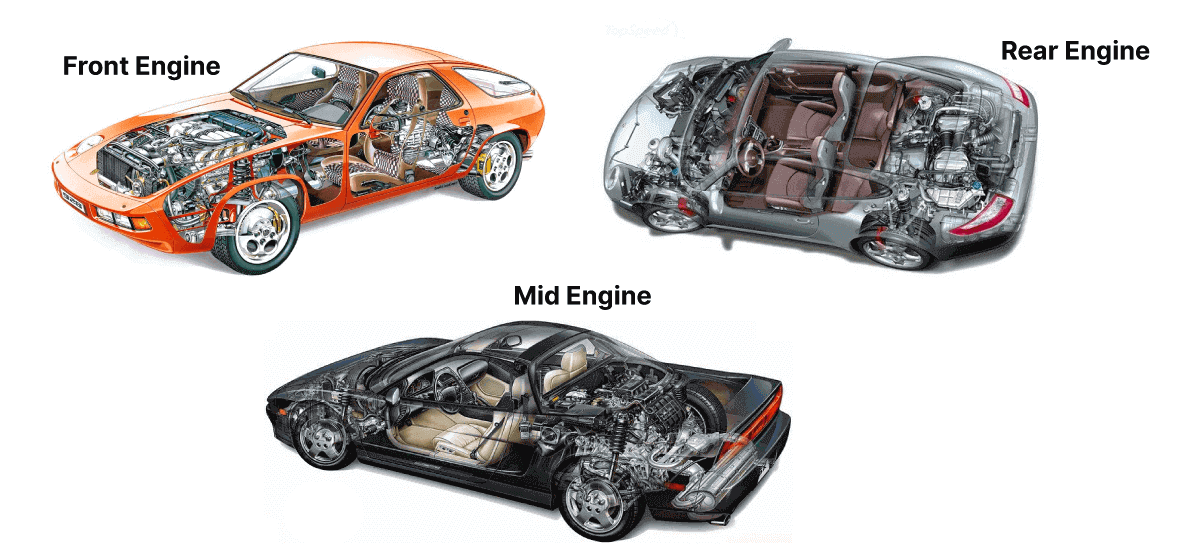
Image Source: World Wide Web
Conclusion
The motor layout is a critical aspect of car design that influences how a vehicle drives, handles, and performs. Whether you’re shopping for a practical family car, an exhilarating sports car, or an innovative electric vehicle, understanding motor layout helps you make an informed decision.
For buyers, it’s not just about horsepower and features—it’s about how the car connects with the road and delivers the experience you desire. Next time you’re on the hunt for your perfect car, remember: where the engine sits matters.
If you’re ready to explore cars with the perfect layout for you, browse our latest models or schedule a test drive today!
( Article / XNmotors Sarah )
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first one to comment.